Open source LLMs are one of the most important AI trends for 2025.
And for good reason:
Open source models were long significantly weaker than proprietary models. But this year they have caught up:
With GPT-OSS-120B, DeepSeek R1, Qwen3-235B-A22B-Thinking, Llama 4 Maverick, and Kimi K2, models have emerged that can compete with the best proprietary LLMs like GPT-5, Claude 4.5, or Gemini 2.5 (and even surpass them in some benchmarks).
In this article, you'll find an overview of the current 50 best open source LLMs with their key benchmark scores and licenses.
Additionally, I'll show you how to easily and freely use open LLMs on your own computer (without needing to program or use the terminal).
- GPT-OSS-120B (OpenAI), DeepSeek R1, and Qwen3-235B lead the 2025 open source rankings, surpassing GPT-4 in many benchmarks (MMLU: 90%+, MATH: 97%+)
- 50 open source LLMs available with various licenses - from MIT to Apache 2.0 to restricted commercial licenses
- New 2025 models like Llama 4 Maverick, Kimi K2, and Gemma 3 27B set new standards for efficiency at smaller model sizes
- Local usage possible with tools like Ollama, LM Studio, or GPT4All - but requires powerful hardware (RTX 4090+ recommended)
Open Source LLMs Compared
Benchmark score color coding:
1. Key Benchmarks Explained
To objectively compare open source LLMs, I use three central benchmark categories:
MMLU / MMLU-Pro: The Massive Multitask Language Understanding Benchmark tests general knowledge across 57 subjects (STEM, social sciences, humanities). MMLU-Pro is the more challenging variant with less contamination. Top models score 85-90% here.
MATH / GPQA: These benchmarks test mathematical and scientific reasoning. MATH-500 contains challenging math problems, while GPQA (Graduate-Level Physics Questions Answers) tests expert knowledge in biology, physics, and chemistry. Top models score 70-97% here.
HumanEval / LiveCodeBench: These benchmarks test code generation. HumanEval contains Python programming tasks, LiveCodeBench tests code performance with current, uncontaminated tasks. Top models score 60-90% here.
The table shows three benchmark scores for each model, which vary depending on the model's strengths (e.g., code-focused models have higher HumanEval scores).
2. Top Models of 2025
GPT-OSS-120B from OpenAI leads the rankings (MMLU: 90.0%, GPQA: 80.1%, AIME: 96.6%) and is the first open-weight model from OpenAI since GPT-2.
DeepSeek R1 with its 671 billion parameters (only 37B active) surpasses GPT-4 in many areas (MMLU: 90.8%, MATH-500: 97.3%) and was trained for just $5.6 million.
Qwen3-235B-A22B-Thinking from Alibaba sets new standards for reasoning (AIME25: 92.3%, LiveCodeBench: 74.1%) and surpasses DeepSeek R1 in 17 out of 23 benchmarks.
Llama 4 Maverick from Meta achieves impressive scores with only 17B active parameters (out of 400B total) (MMLU-Pro: 80.5%, GPQA: 69.8%) and beats significantly larger models.
3. LLM Licenses Explained
Here's an overview of the most commonly used licenses for open source LLMs.
MIT License
A very permissive open source license, similar to Apache 2.0. It allows unrestricted use, modification, and distribution of the LLM, including in proprietary programs, as long as the copyright notice is retained. DeepSeek V3 uses MIT with some restrictions for military use.
Llama 2 Community / Llama 3 Community
Meta released Llama 2 and Llama 3 under these licenses. They allow free use of the LLMs for research and commercial applications with up to 700 million monthly active users. The source code and model weights are freely available.
Qwen License / Qianwen LICENSE
Qwen models are released under various licenses. While smaller models are often licensed under Apache 2.0, larger models like Qwen2.5-72B have special license terms that allow commercial use with certain restrictions.
Apache 2.0
A very permissive open source license with minimal restrictions. It allows use, modification, and distribution of the LLM, including in proprietary programs, as long as the copyright notice is retained. It contains no copyleft clause.
CC BY-NC-4.0
A Creative Commons license that allows editing and sharing the LLM in any form, but not for commercial purposes. The author's name must be credited.
CC BY-NC-SA-4.0
Similar to CC BY-NC-4.0, but with the additional Share-Alike condition. This means forks or modified versions of an LLM must be distributed under the same conditions.
Non-Commercial
Here, using the LLM for commercial purposes is prohibited. However, what exactly counts as "commercial" is not always clearly defined or delimited.
Usually, "non-commercial" models are only released for research purposes or private use.
4. Using Open Source LLMs Locally on Your Own Computer
Using open source LLMs locally on your own computer is easier than you might think:
1. Download LM Studio
Download LM Studio from the website. It's free and available for Mac, Windows, and Linux:
2. Install and Open LM Studio
Next, install LM Studio on your computer and open it.
3. Download Your Desired Open Source LLMs
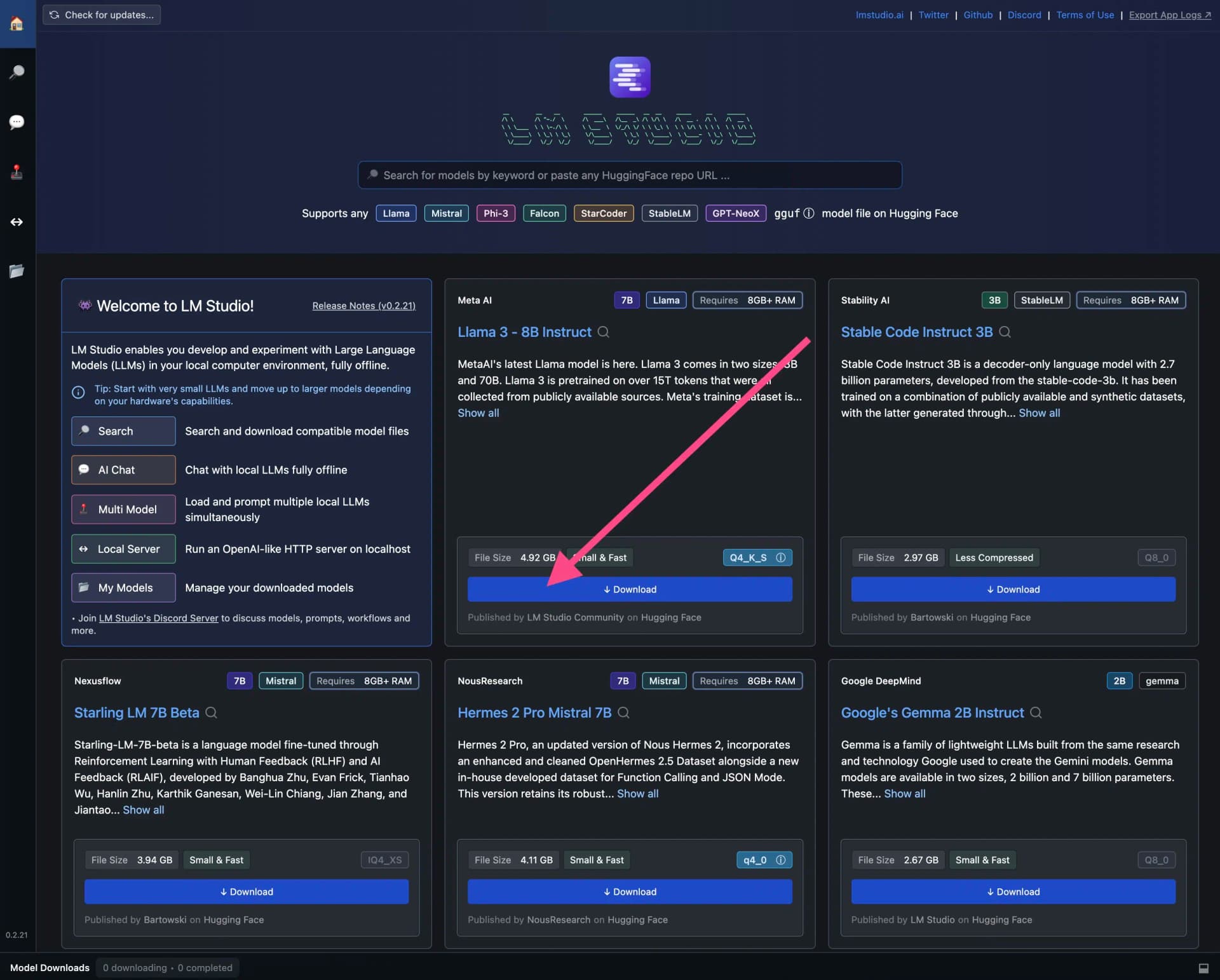
Now you need to download the open source LLMs you want to use in LM Studio.
Many popular LLMs are already on the home screen. To download an LLM, simply click the blue download button:
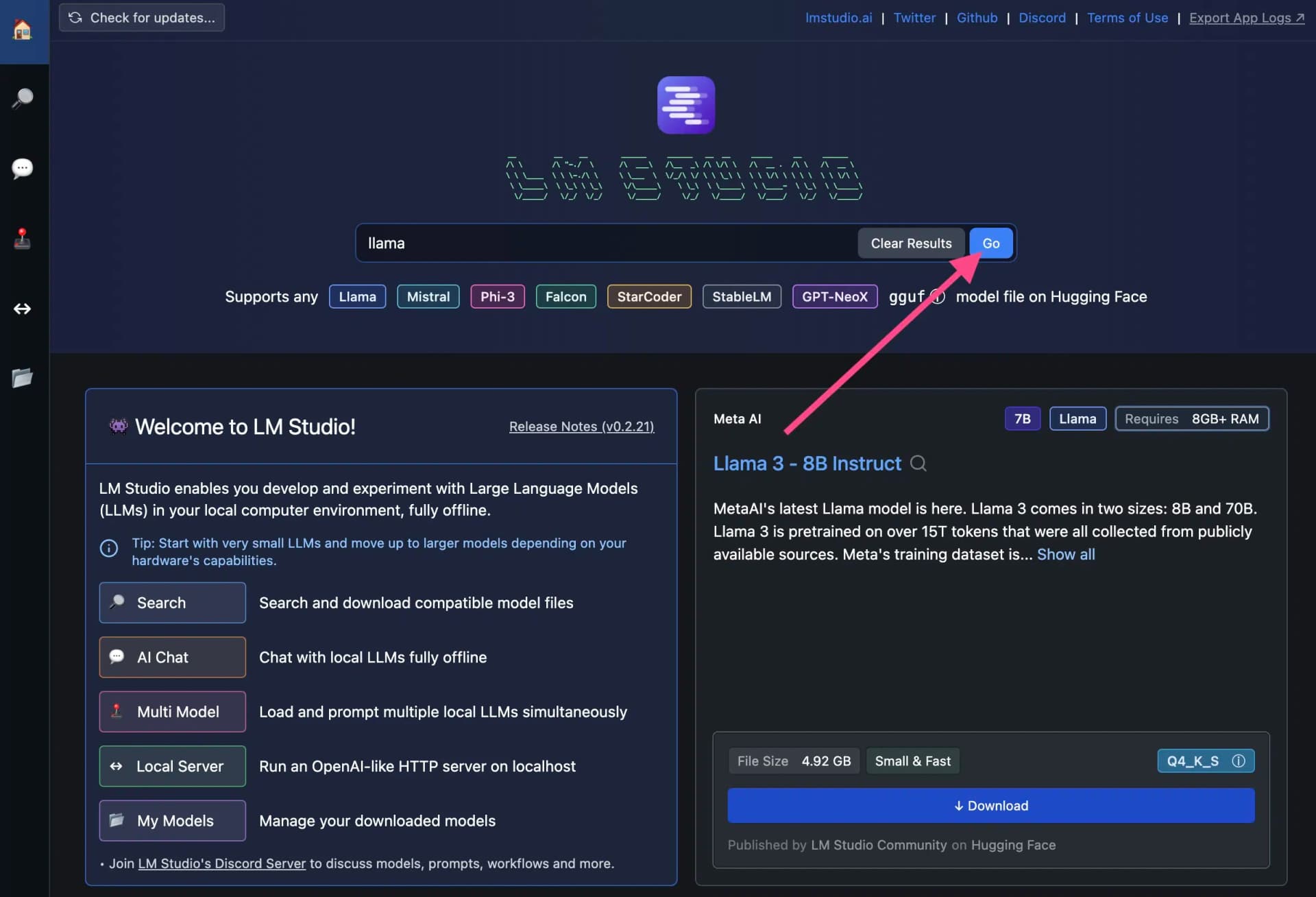
To find specific open source LLMs, you can also use the search function:
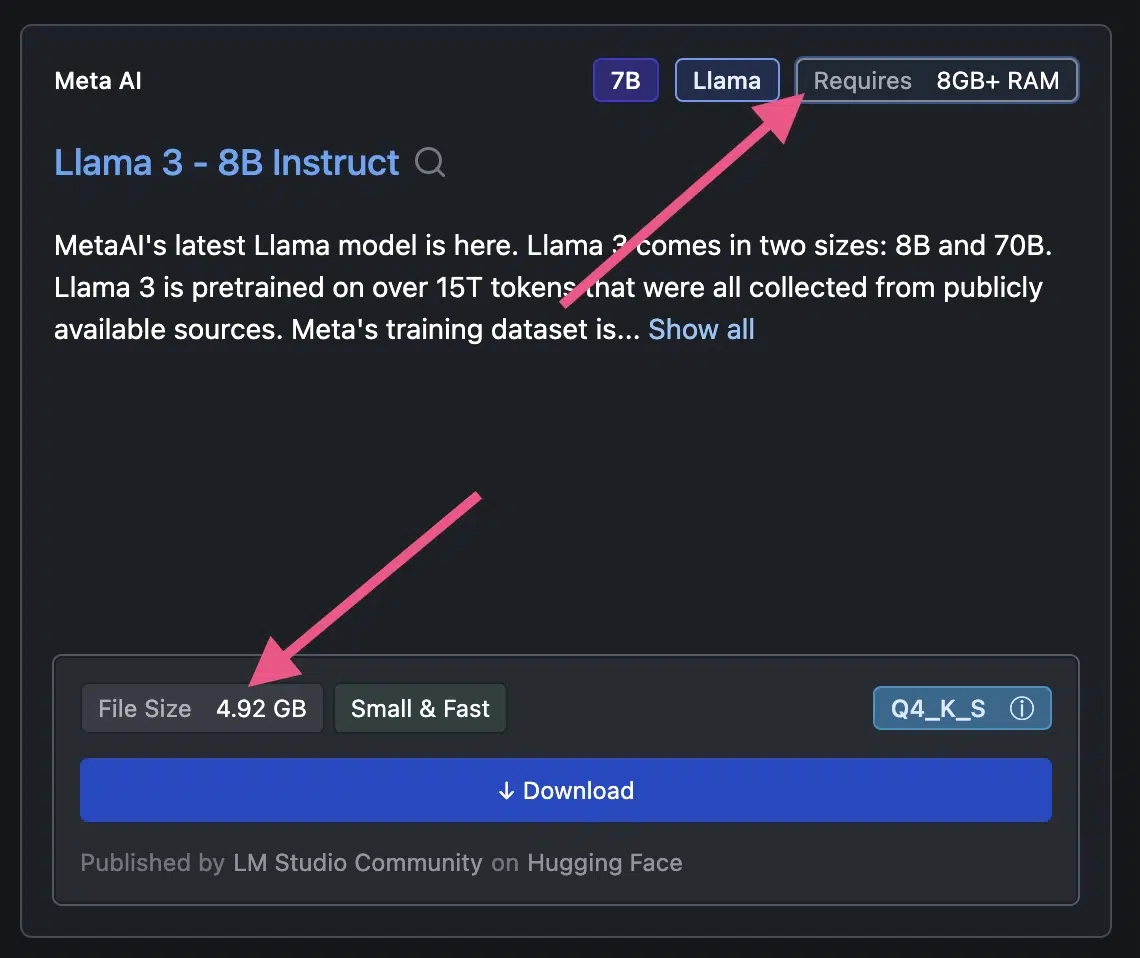
4. Important: Check System Requirements Before Downloading
Before downloading an LLM, you should check the system requirements.
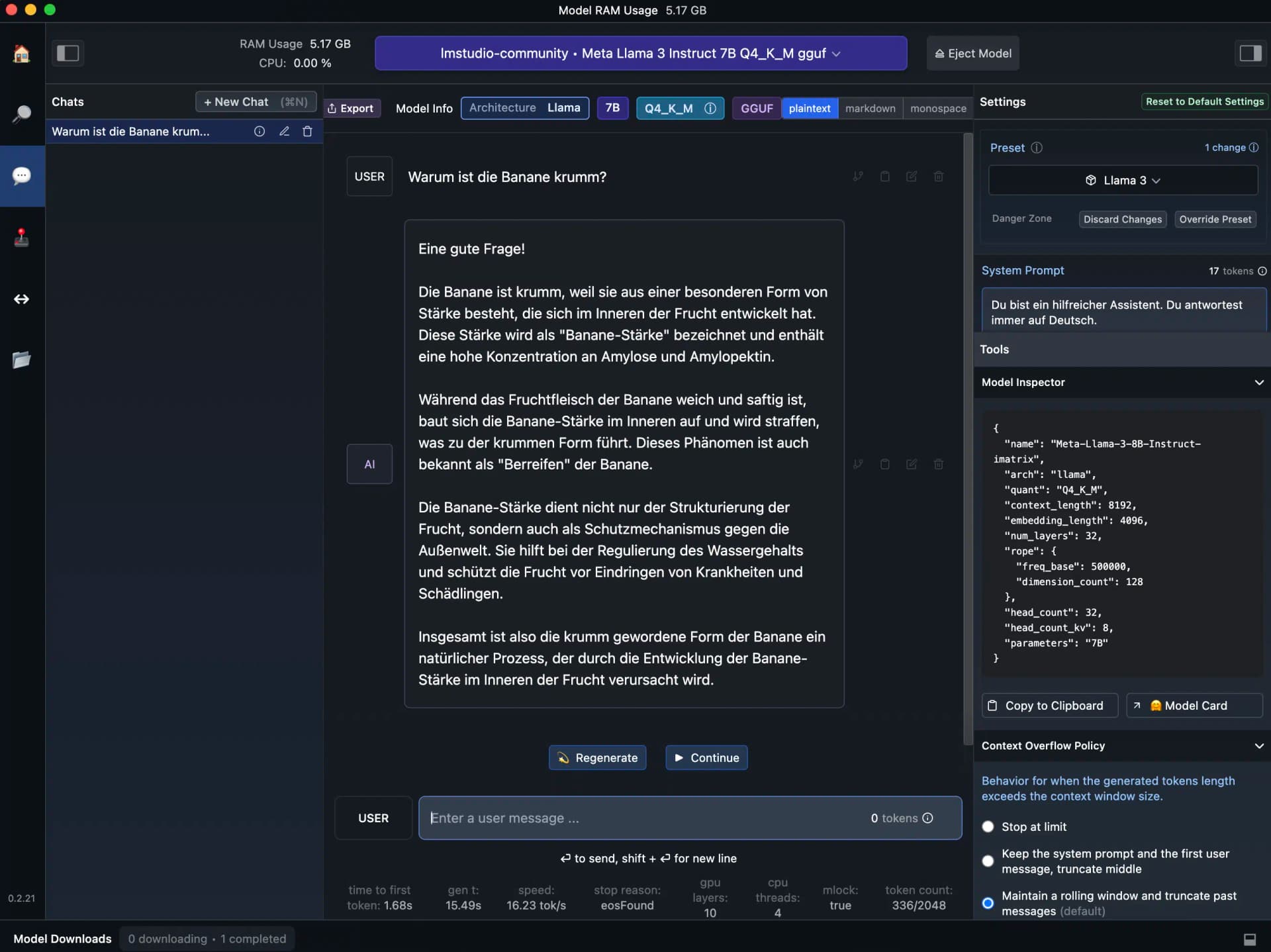
Llama 3, for example, requires more than 8 GB RAM and 4.92 GB of free storage:
5. Chat with the Open Source LLM
After downloading an open source LLM, you can use it directly in LM Studio.
Simply click on the speech bubble icon (?) in the left sidebar.
The user interface and settings options are reminiscent of the OpenAI Playground: